
















This chapter explains the process of expressing amounts denominated in one currency in terms of a second currency, by using the exchange rate between the currencies. As per ASC 830 (was FAS 52), assets and liabilities are translated at the current exchange rate at the balance sheet date. Income statement items are typically translated at the weighted-average exchange rate for the period.
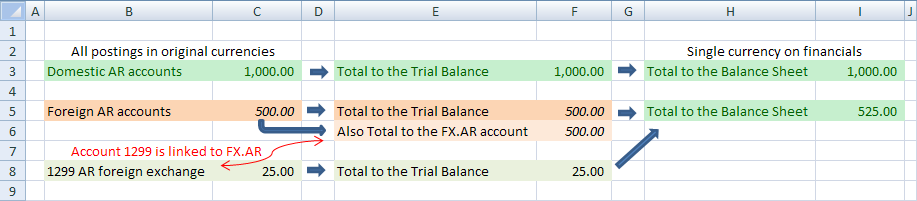
The spreadsheet below illustrates the concept used in synchronizing foreign currency transactions into a single reporting currency. NewViews tracks your transactions as posted in their original (non converted/functional) currency through your total to structure. NewViews then uses the Tools>Foreign_Currency command to periodically synchronize your books with journal entries.
Within a set of books, Foreign Currencies may be handled in several ways.
One determining point is, do your books have a Bank account in a foreign currency?
If you do not have a foreign currency bank account, then the Basic Method may be suitable.
If you do have a foreign currency bank account, then the Intermediate Method may be suitable.
This method may be sufficient if you only deal with a hand full of foreign currency transactions per year.
Enter all foreign currency transactions converted to the domestic currency. Use a single expense account to post the exchange gain / loss.
All the reports should reflect the current domestic balances, nothing else needs to be done. You may skip this chapter.
If you do have a bank account with a foreign currency, then you may be displaying mixed currency values in your reports. Method 2 below explains in detail how to add multiple foreign exchange accounts to convert reports to a single currency.
All domestic transactions are posted in their original reporting currency. Foreign currency transactions are posted to foreign currency accounts. All foreign currency accounts are sub-grouped and totaled to a foreign currency report. Currency conversion accounts are adjusted for each sub-group. This solution to foreign exchange is based on periodic journal entries that reset the financial reports to a single currency.
This is accomplished by adding a short list of accounts, a foreign exchange report and periodic journal entries.
The journal entries adjusts the period end balances of the Bank, AR and AP accounts, as well as translating the period amounts of Sales and Expenses.
Any number of foreign currencies can be handled simultaneously in the same set of books.
The Canadian demobooks have foreign exchange accounts, a report and sample foreign exchange transactions. See Demobooks for more.